Flat Feet, Pronated Feet, Rolled in Feet
Flat feet or Pronated Feet or Rolled-in Feet usually have quite flexible joints and the range of motion to roll in or collapse through the arches
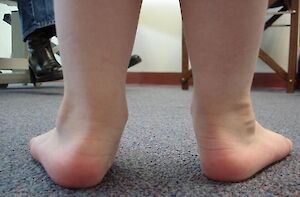
Flat feet or Pronated Feet or Rolled-in Feet usually have quite flexible joints and the range of motion to roll in or collapse through the arches. In children under the age of 2 years, it is normal to have flat chubby feet but by 2 years of age, some development of an arch should be visible.
This foot type in children often requires more muscle energy than normal during gait to maintain unstable joints thus resulting in fatigue or tired aching feet and legs, so the children who don’t want to walk far or want to be carried. Pronated feet or rolled-in feet, do not necessarily always result in a lowered or flat arch. Pronation is the motion of the joints in the rear foot that controls to some degree how the whole foot operates.
Feet that pronate during gait appear to be rolled in at the heels and medial ankle and sometimes have a lowered arch but not always, and there is excessive pressure under the ball of the big toes when stepping forward. Pronation at the foot can also result in internal rotation at the legs and knees. There are many symptoms or foot conditions that can be as a result or contributed to by pronated feet and your podiatrist can assess and explain how your child’s feet function and the related issues and then advise on the best treatment plan to suit your child’s feet. Orthotic therapy is often indicated with flat feet, pronated or rolled-in feet.
Pronated feet don’t always present with pain especially with children however a range of potential issues related to pronated feet may occur at some stage. Our experienced Podiatrists are able to advise you on preventative orthotic therapy related to your child’s feet also considering their hereditary history and activities including sports and dance.
Ready to meet the team and make an appointment?
Online Booking is the quickest most convenient way to secure the time, location and practitioner you want. Want to meet your Practitioner first? Select Meet the Team to get to know our amazing Podiatrists.